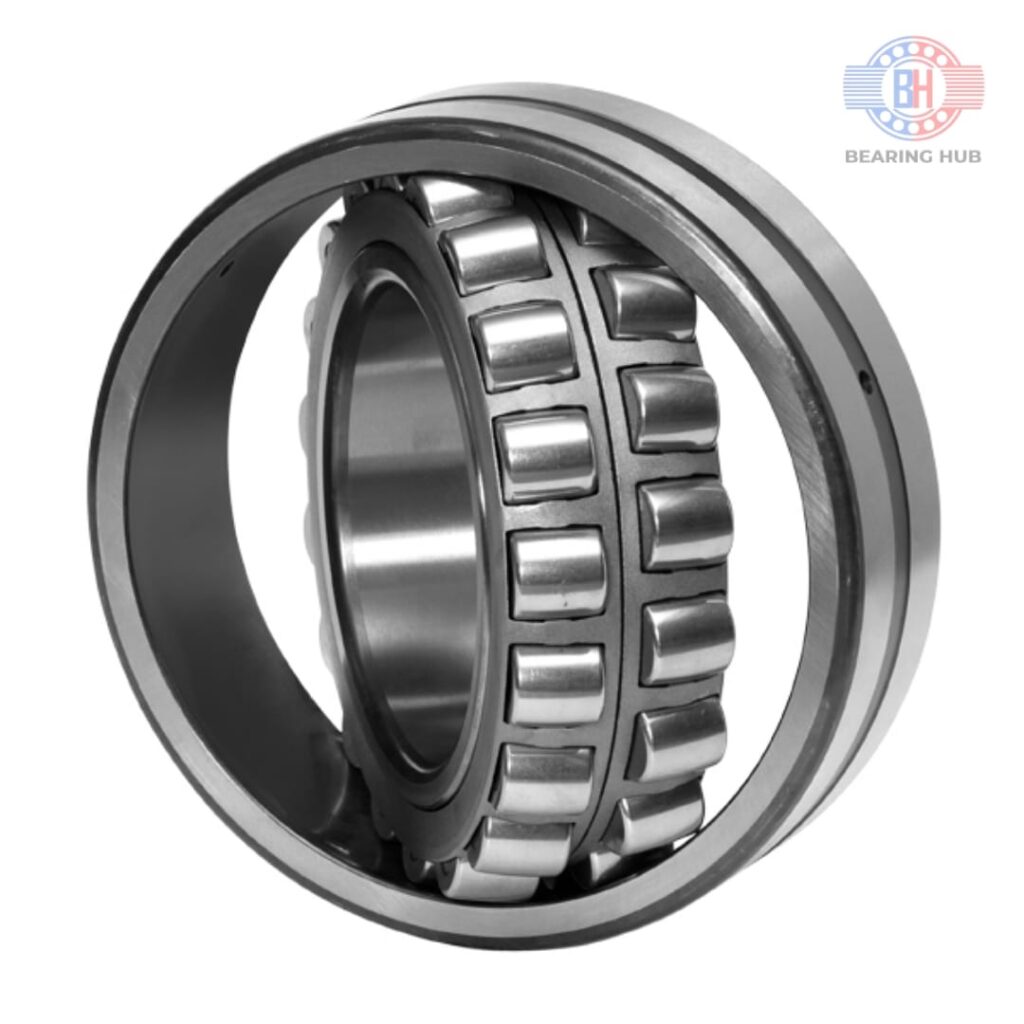



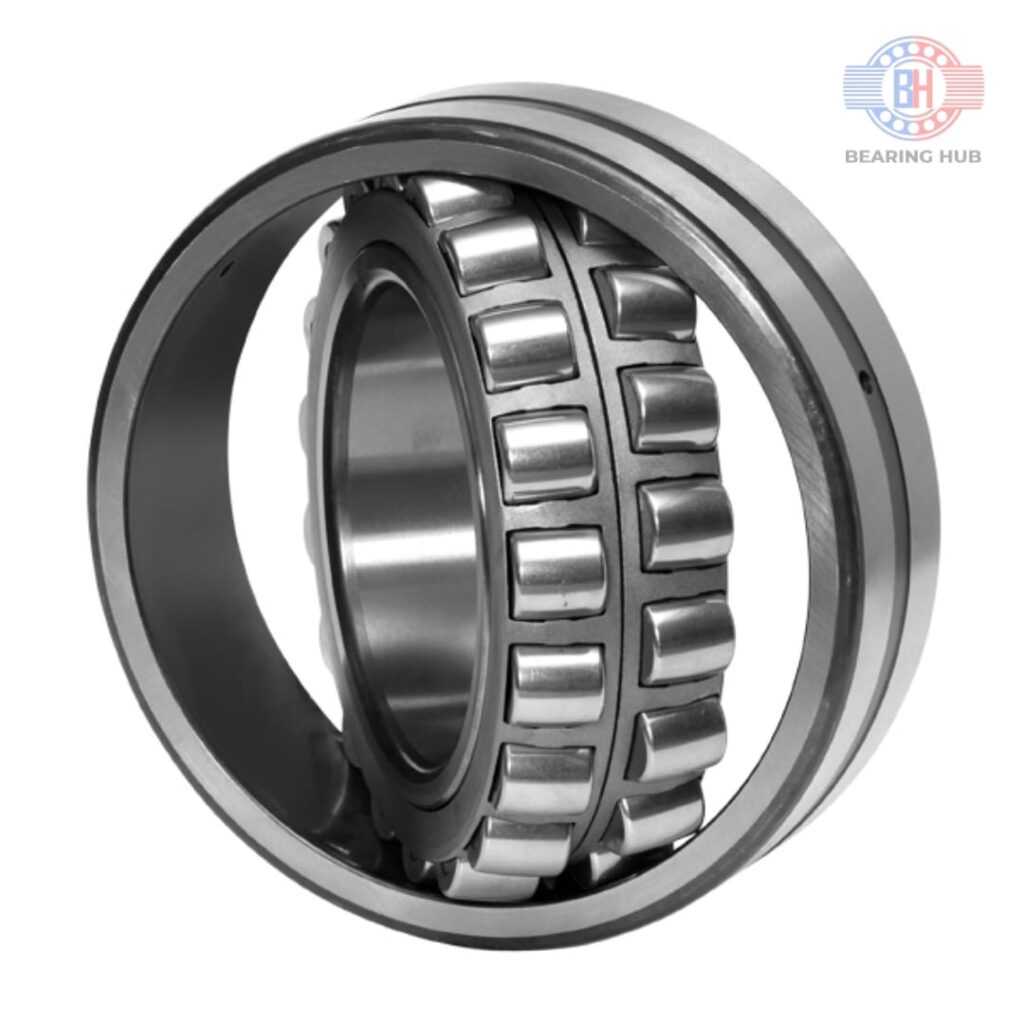
The main purpose of bearings is to prevent direct metal-to-metal contact between two elements that are in relative motion. This prevents friction, heat generation and ultimately, the wear and tear of parts. It also reduces energy consumption as sliding motion is replaced with low-friction rolling.
They also transmit the load of the rotating element to the housing. This load may be radial, axial, or a combination of both. A bearing also restricts the freedom of movement of moving parts to predefined directions as discussed above.
Rolling element bearings contain rolling elements in the shape of balls or cylinders. We know that it is easier to roll a wheel than slide it on the ground as the magnitude of rolling friction is lower than sliding friction. The same principle is in work here. Rolling element bearings are used to facilitate the free movement of parts in rotational motion.
Our Product
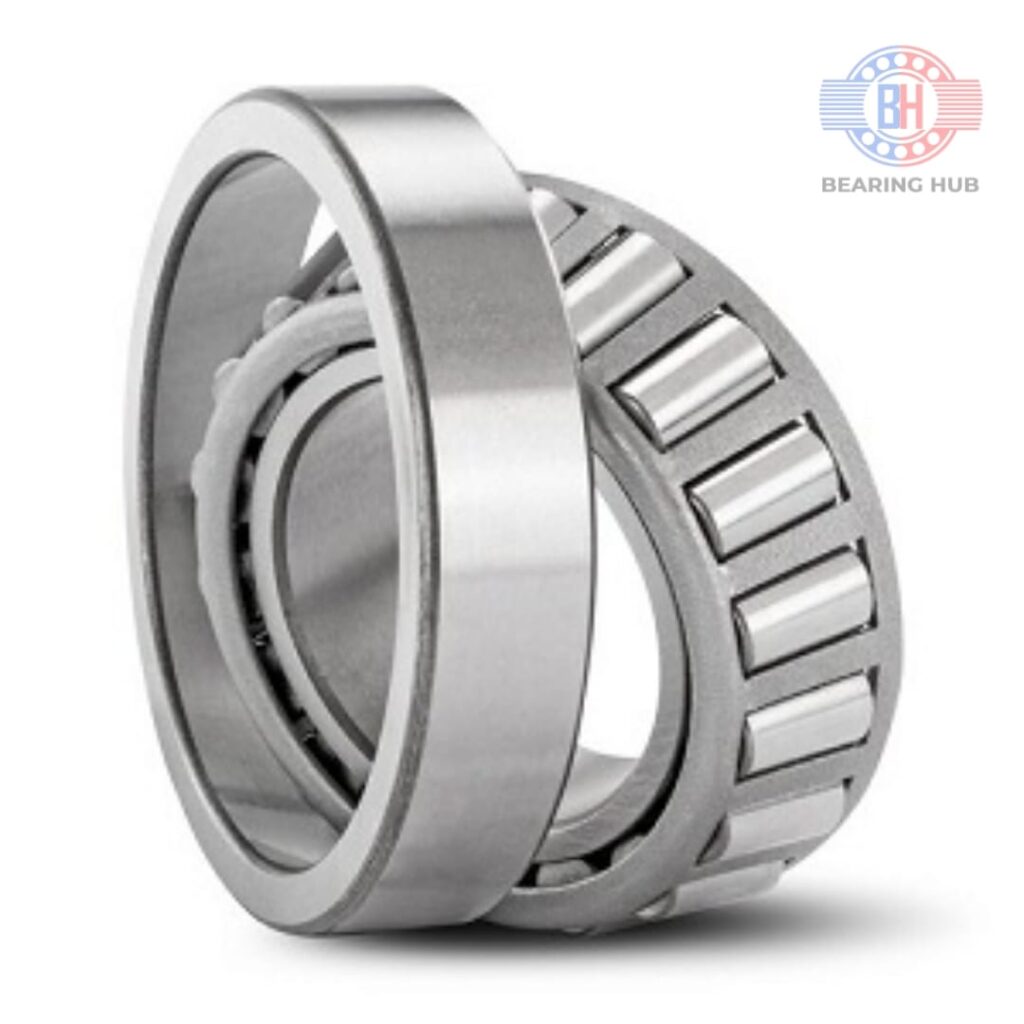
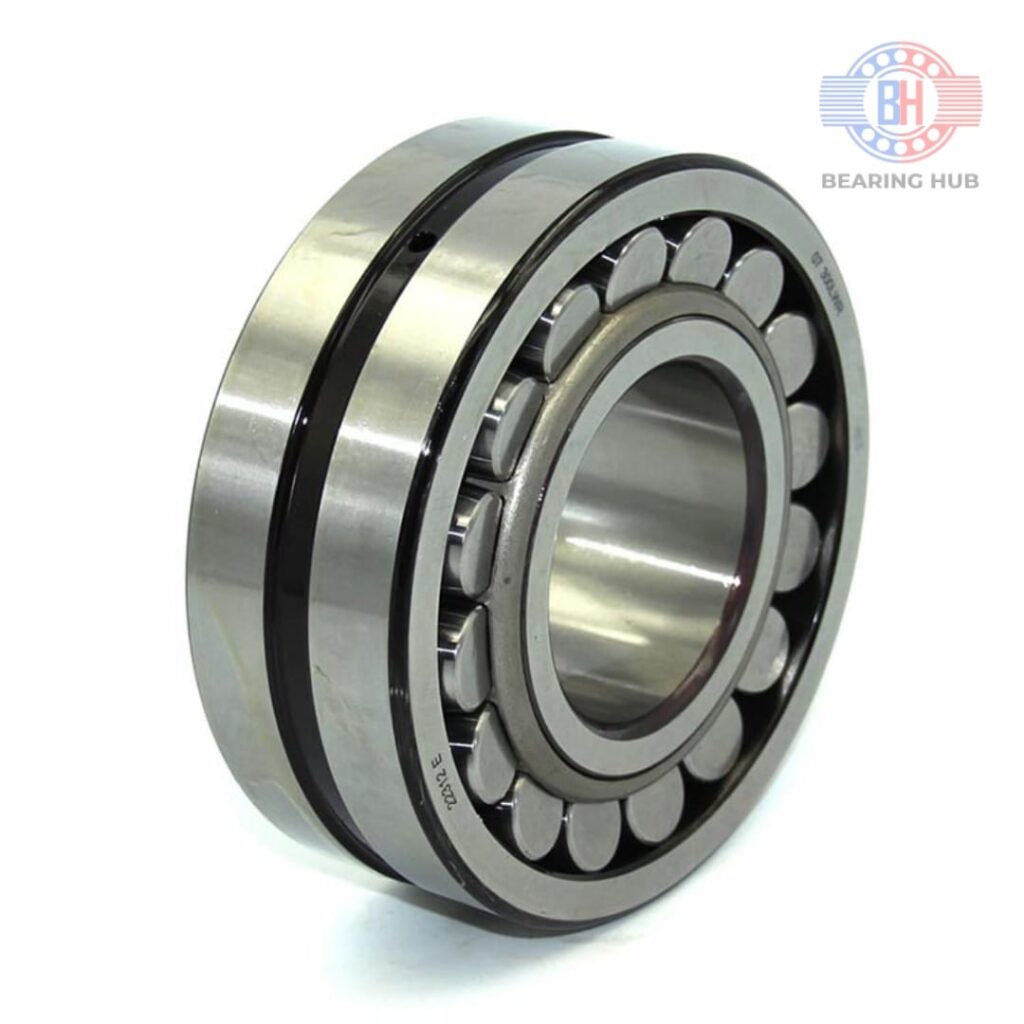



Frequently Asked Questions
Precision and high-precision ball bearings are both types of bearings designed to reduce friction between moving parts in machines and equipment, but they differ in terms of their manufacturing tolerances and performance specifications. Precision ball bearings are manufactured to tight tolerances that allow for high levels of accuracy and consistency in their performance. They are typically used in applications that require a moderate level of precision, such as in electric motors, pumps, and conveyor systems.
The most important factor for determining the shelf life of a “properly stored” bearing is the lubrication. Greases and oils do have shelf lives (expiration dates). This is discussed in detail in our white paper entitled.
Otherwise, providing the bearing is stored poperly (typically in its original factory packaging), the potential effects of contamination and oxidation will be minimal and not significantly effect shelf life.
Did we miss something? If you have another question for us, just let us know and we will do our best to provide you a prompt and accurate answer. AST Bearings provides “value beyond the part.”
- Project objectives: Define the project’s objectives, including the required specifications and performance requirements of the bearing.
- Stakeholder identification: Identify all stakeholders, including suppliers, manufacturers, designers, and end-users, and establish communication channels with them.
- Risk management: Identify potential risks that could impact the bearing’s performance, and develop contingency plans to mitigate these risks.
Material quality: The quality of the material used to manufacture the bearing can significantly impact its performance. High-quality materials, such as chrome steel, can improve the bearing’s durability, load capacity, and resistance to wear and corrosion.
Lubrication: Proper lubrication can help reduce friction and wear between the bearing’s rolling elements and raceways. Adequate lubrication also helps prevent contamination and corrosion, which can negatively impact the bearing’s performance.
Design: The design of the bearing plays a crucial role in its performance. The bearing’s design should be optimized for the specific application and operating conditions, including load capacity, speed, temperature, and vibration.
Thin section bearings are used in applications where space is limited and a compact design is required. They are characterized by their small cross-section and high stiffness, making them ideal for applications where high precision and load-carrying capacity are essential. Some common uses of thin section bearings include
Robotics: Thin section bearings are commonly used in robotics and automation applications, where they can provide high-precision motion control in tight spaces.
Aerospace: Thin section bearings are used in aerospace applications, such as aircraft landing gear, where their high stiffness and load-carrying capacity are critical.
Our Success Story
Start
Increased revenue: A company may achieve this by increasing sales or expanding its customer base.
process
Cost savings: A business might achieve cost savings through more efficient operations, reducing waste, or negotiating better supplier contracts.
progress
Product innovation: A business may achieve this by developing new products or services that meet customer needs or create new market opportunities.
Groth
Improved customer satisfaction: A company might achieve this by improving customer service, enhancing the user experience of its products or services, or addressing customer complaints and concerns.